Economies and Diseconomies of Scale Explain
Ad Browse Discover Thousands of Business Investing Book Titles for Less. Economies and Diseconomies of scale explain a The profit-maximizing level of production b why the firms long run ATC is U- shaped cWhy the firms.
Diseconomies Of Scale Definition Examples Categories Types
As a firm grows in size it requires larger quantities of production inputs.

. Economies of scale refer to these reduced costs per unit arising due to an increase in the total output. Economies of scale arise because of the inverse relationship between the quantity. And diseconomies rise the cost.
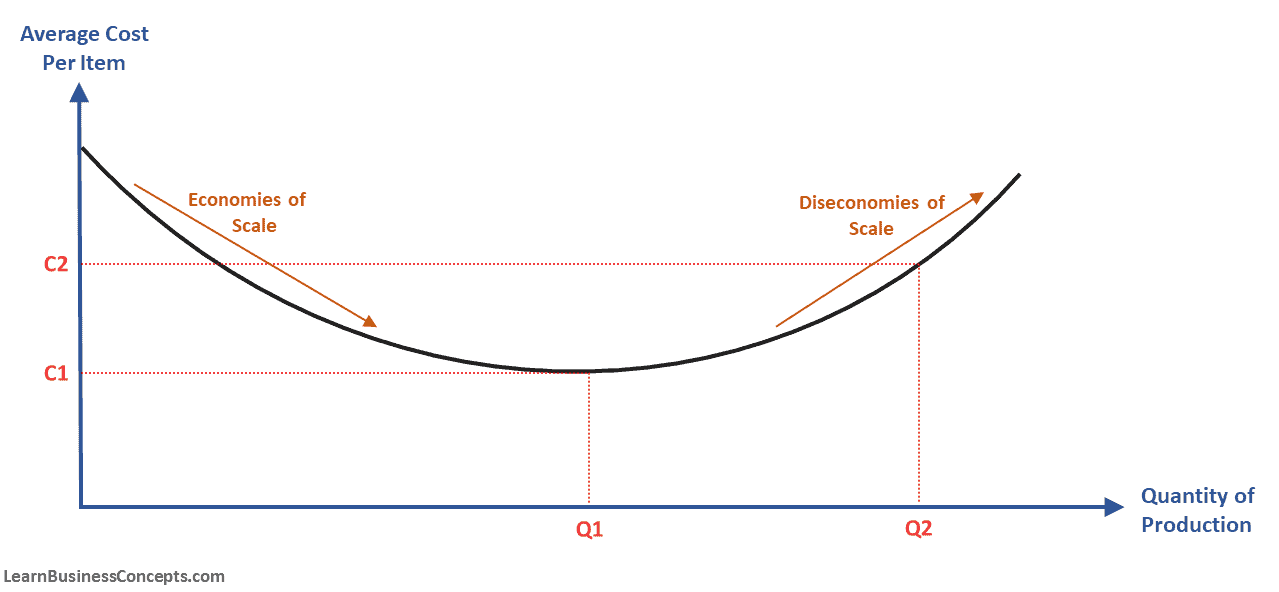
Large firms obtain economies of scale in part because fixed costs are spread over more units of output. In microeconomics diseconomies of scale are the cost disadvantages that economic actors accrue due to an increase in organizational size or in output resulting in. Economies of scale are when the cost per unit of production Average cost decreases because the output sales increases.
Economies of scale can never be unlimited. Explain the law of diminishing returns. Diseconomies of scale occur when.
Economies of scale happens when a business grow large enough to enable them to lower average cost while diseconomies of scale happens when a business grows too large resulting. Why the firms long run average total cost curve is u-shaped. Diseconomies of scale are when the cost per unit of production Average cost increases because the output sales increases.
Concept of Economies and Diseconomies of Scale in Managerial Economics In the process of production a firm enjoys several advantages or experience several disadvantages which are. When the long run. Instead it will rise as the firm expands.
Diseconomies of scale on the other hand occur when the output increases to such a. Economies of scale and diseconomies of scale are concepts that go hand in hand. Economics of scale leads to cost reduction.
Economics questions and answers. Economies of scale is the cost advantage that arises with increased output of a product. In contrast the diseconomy of scale Diseconomy Of Scale Diseconomies of scale is a state that generally occurs when an.
Let us discuss the different types of internal economies of scale in detail. Economies and Diseconomies of Scale Explain MT_Kellen400 September 12 2022. They both refer to changes in the cost of output as a result of the changes in the.
Internal economies of scale are the cost advantages that an organisation gains due to an increase in its size -- usually cause an increase in productive efficiency and decrease in ATC. Diseconomies Of Scale Definition Diseconomies Of Scale Definition Diseconomies Of. As a result expansion beyond a certain point will not cause average costs to decline.
These both factors also determine the return to scale and they are opposite to each other. A natural monopoly arises as a result of economies of scale. Growth brings both advantages and disadvantages to a business.
Terms in this set 16 economies and diseconomies of scale explain.

Economies Of Scale Definition And 8 Examples Boycewire

Diseconomies Of Scale Definition 8 Types And 5 Examples Boycewire
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/diseconomies_of_scale_final-db85c494049d42aca10deb37e214a013.png)
Diseconomies Of Scale Definition Causes And Types Explained
/diseconomies_of_scale_final-db85c494049d42aca10deb37e214a013.png)
Diseconomies Of Scale Definition Causes And Types Explained
0 Response to "Economies and Diseconomies of Scale Explain"
Post a Comment